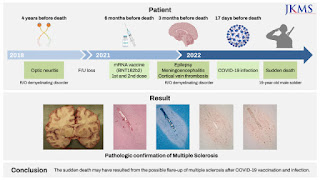
Pulmonary manifestations of vaccination
A previously healthy 46-year-old woman who never had COVID-19, developed pleuritic chest pain on the tenth day after receiving the third dose of BNT162b2 and was subsequently admitted to the emergency department. Physical examination of the chest revealed a unilateral pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid in the pleural space). During the focused lung ultrasound, a small left pleural effusion was detected by placing the transducer in the left posterior axillary line at the lower part of the chest (zone L3). She was negative to influenza A, A/H1, A/H3, B; Adenovirus; coronavirus HKU1, NL63, 229E, OC43; parainfluenza virus types 1, 2, 3, 4; RSV; human rhinovirus/enterovirus; human metapneumovirus, Middle East respiratory syncytial coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2 as well as bacteria bordetella pertussis, bordetella parapertussis, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. She was also negative to antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA), rheumatoid f...